Eating more healthily and having a moderate cut in calories combined with more exercise each day should lead to gradual maintained weight loss.
A combination of both diet and exercise has been proven to be most effective over a long term period.
Many types of physical activity can support weight loss by increasing the amount of calories that you burn. The amount of weight you can expect to lose may vary depending on your age, diet, and starting weight.
Ideally, you want to lose the fat and gain muscle instead so measures of body composition such as skinfold tests or waist circumference measures may be more helpful and encouraging than looking at the scales.

How can physiotherapy be used in slimming?
Physiotherapy recognises the barriers to activity and movement of a person and then deals with these problems first to lead to effective weight loss.
It also aims to manage associated problems like arthritis, back pain and stiffness through exercise to increase the movement of an individual which will automatically lead to greater physical activity which will help in maintaining weight loss.
Education on strategies for adherence to an independent exercise program is also recommended whenever possible.
Follow up exercise programs tend to be more effective if individually designed and supervised and combined with regular follow up. Follow up is critical for maintaining motivational levels, progressing the activity, and modifying the exercise program if circumstances change.
Physiotherapy management
Recommended evidence-based approach for the physiotherapy management of overweight and obesity.
- Assessment of the individual’s medical history
- Evaluation of current physical activity level
- Provision of an individualised physical activity program
- Gradual progression of a physical activity program
- Prescription of a cardiovascular training program
- Prescription of resistance exercises
- Prescription of moderate-intensity physical activity, 30 min/d, 3–5 d/wk
In addition to helping you lose weight, exercise has many other benefits, including improved mood, stronger bones, and a reduced risk of many chronic diseases
1. Walking
It’s a convenient and easy way for beginners to start exercising without feeling overwhelmed or needing to purchase equipment. Also, it’s a lower-impact exercise, meaning it doesn’t stress your joints.
A 12-week study of 20 women with obesity found that walking for 50–70 minutes 3 times per week reduced body fat and waist circumference by an average of 1.5% and 1.1 inches (2.8 cm), respectively .
It’s easy to fit walking into your daily routine. To add more steps to your day, try walking during your lunch break, taking the stairs at work, or taking your dog for extra walks.
To get started, aim to walk for 30 minutes 3–4 times a week. You can gradually increase the duration or frequency of your walks as you become more fit.
2. Jogging or running
Jogging and running are great exercises to help you lose weight.
Although they seem similar, the key difference is that a jogging pace is generally between 4–6 mph (6.4–9.7 km/h), while a running pace is faster than 6 mph (9.7 km/h).
What’s more, studies have found that jogging and running can help burn visceral fat, commonly known as belly fat. This type of fat wraps around your internal organs and has links to various chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes (7Trusted Source, 8Trusted Source, 9Trusted Source).
Both jogging and running are great exercises that can be done anywhere and are easy to incorporate into your weekly routine. To get started, aim to jog for 20–30 minutes 3–4 times per week.
If you find jogging or running outdoors hard on your joints, try running on softer surfaces like grass. Also, many treadmills have built-in cushioning, which may be easier on your joints.
4. Weight training
Weight training is a popular choice for people looking to lose weight.
Also, weight training can help you build strength and promote muscle growth, which can raise your resting metabolic rate (RMR), or how many calories your body burns at rest
Another study found that 24 weeks of weight training led to a 9% increase in metabolic rate among men, which equated to burning approximately 140 more calories per day. Among women, the increase in metabolic rate was nearly 4%, or 50 more calories per day.
In addition, studies have shown that your body continues to burn calories many hours after a weight-training workout, compared with aerobic exercise.
5. Interval training
Interval training, more commonly known as high intensity interval training (HIIT), is a broad term for short bursts of intense exercise that alternate with recovery periods.
Typically, a HIIT workout lasts 10–30 minutes and can burn many calories.
One study of 9 active men found that HIIT burned 25–30% more calories per minute than other types of exercises, including weight training, cycling, and running on a treadmill
That means HIIT can help you burn more calories while spending less time exercising.
Furthermore, numerous studies have shown that HIIT is especially effective at burning belly fat, which has links to many chronic diseases
HIIT is easy to incorporate into your exercise routine. All you need to do is choose a type of exercise, such as running, jumping, or biking, and your exercise and rest times.
For example, pedal as hard as you can on a bike for 30 seconds, followed by pedaling at a slow pace for 1–2 minutes. Repeat this pattern for 10–30 minutes.
7. Yoga
Yoga is a popular way to exercise and relieve stress.
While it’s not commonly thought of as a weight loss exercise, it burns a fair amount of calories and offers many additional health benefits that can promote weight loss.
Additionally, the yoga group experienced improvements in mental and physical well-being.
Aside from burning calories, studies have shown that yoga can teach mindfulness and reduce stress levels. (22Trusted Source).
Yoga is a great weight loss exercise that you can perform almost anywhere.
8. Pilates
Pilates is a great beginner-friendly exercise that may help you lose weight.
Although Pilates may not burn as many calories as aerobic exercises like running, many people find it enjoyable, which makes it easier to stick to over time.
Other than weight loss, Pilates may reduce lower back pain and improve your strength, balance, flexibility, endurance, and overall fitness level
Pilates is a great beginner-friendly exercise that can help you lose weight while improving other areas of your physical fitness.
More…
You should aim to lose no more than 0.5kg per week. Faster weight loss is good in the short term but is very difficult to maintain and people usually regain the weight afterwards.
Exercise has additional benefits other than just burning calories. Regular exercise reduces the number of inflammatory chemicals and increases anti-inflammatory chemicals in the body which may also reduce pain.
Research has shown that diet changes attribute 60-80% of weight loss, while exercise only contributes about 10-20% of weight loss
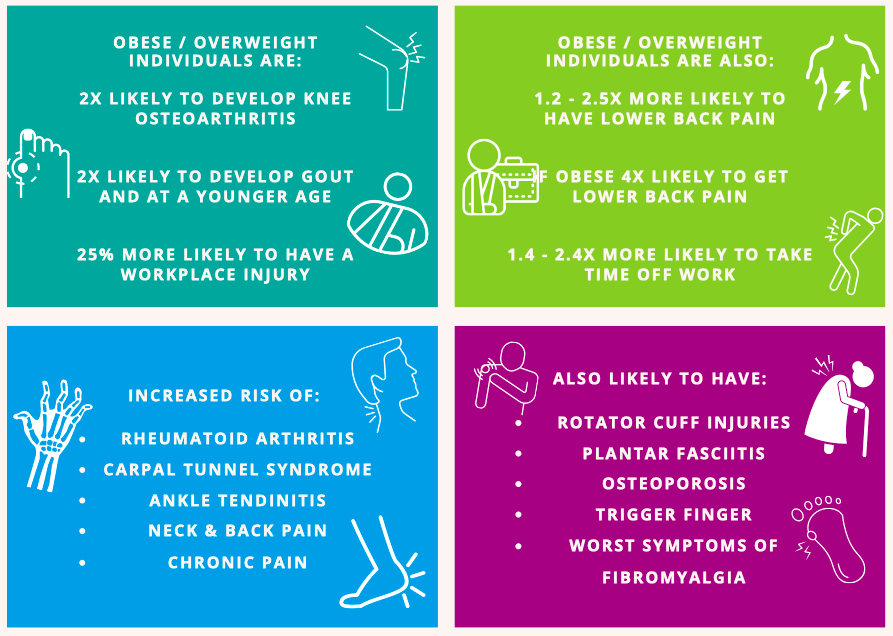
How can body fat impact on musculoskeletal pain?
Excess fat- fatty tissues are thought to be a source of inflammatory chemicals in our bodies that can contribute to inflammation which negatively impacts multiple systems in the body, including increasing joint pain.
This explains why high levels of body fat are associated with osteoarthritis in non-weight bearing joints such as hands, where the loading isn’t weight related as it is in the knee.
What should you do to reduce your risk of body pain?
Body fat, and not BMI, is a more accurate predictor of musculoskeletal pain, especially osteoarthritis.
So to reduce your risk – focus on reducing your body fat, and try to maintain muscle mass. This might mean that you lose less weight overall but achieve a bigger reduction in your percentage of body fat, decreasing the level of inflammation in your system and consequently reducing your pain.
Obesity and Osteoarthritis
Obesity in early life predicts Osteo Arthritis (OA) many years later
For people with OA, weight loss improves symptoms and slows disease progression
For those who have joint replacements due to OA being over weight or obese is linked with additional complications, such as:
Those who are morbidly obese benefit less from the surgery
Artificial joints do not last as long in those who are obese
Increased body weight increases the risk of surgical complications, longer hospital stays, major complications and higher rates of readmission after discharge